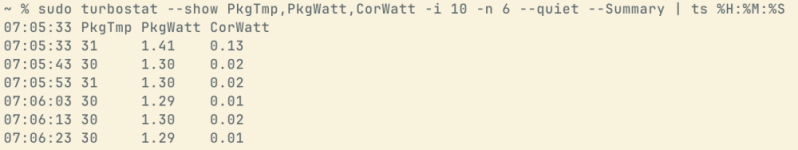
9th and 10th gen are both derivatives of Skylake.
11th is Rocket Lake (Cypress Cove), which is a backported Ice Lake (Sunny Cove) with some improvements. This is a different microarchitecture than Skylake.
12th is Alder Lake, which is Golden Cove.
This is a comparison of all four generations on Intel's website:
Intel® product specifications, features and compatibility quick reference guide and code name decoder. Compare products including processors, desktop boards, server products and networking products.

ark.intel.com
Why Intel orders them 12, 9, 10, 11, is a mystery, but you can see what has been added/removed over time. All of them have AES-NI.
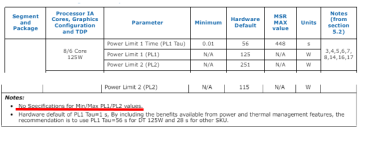
The only difference between a -K and a non-K CPU on boards that apply no limits is that the non-K CPUs have significantly lower base clocks, and lower boost clocks. Since the boost clocks are what push the CPU far beyond the sweet spot of the voltage/frequency curve, the non-K parts are less likely to burn themselves out, even when unlimited.